0708-1300/Class notes for Tuesday, September 11: Difference between revisions
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
If <math>f:V\rightarrow W</math> and <math>g:U\rightarrow V</math> are ''diffable'' maps then the following asertions holds: |
If <math>f:V\rightarrow W</math> and <math>g:U\rightarrow V</math> are ''diffable'' maps then the following asertions holds: |
||
# <math>df_{x}</math> is unique. |
|||
# <math>d(f+g)_{x}=df_{x}+dg_{x}</math> |
|||
# If <math>f</math> is linear then <math>df_{x}=f</math> |
|||
# <math>d(f\circ g)_{x}=df_{g(x)}\circ dg_{x}</math> |
|||
# For every scalar number <math>\alpha</math> it holds <math>d(\alpha f)_{x}=\alpha df_{x}</math> |
|||
===Implicit Function Theorem=== |
===Implicit Function Theorem=== |
||
Revision as of 17:36, 11 September 2007
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In Small Scales, Everything's Linear
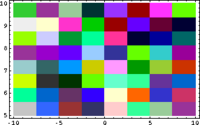
|
[math]\displaystyle{ \longrightarrow }[/math] | 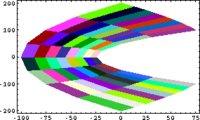
|
| [math]\displaystyle{ z }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \mapsto }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ z^2 }[/math] |
Code in Mathematica:
QuiltPlot[{f_,g_}, {x_, xmin_, xmax_, nx_}, {y_, ymin_, ymax_, ny_}] :=
Module[
{dx, dy, grid, ix, iy},
SeedRandom[1];
dx=(xmax-xmin)/nx;
dy=(ymax-ymin)/ny;
grid = Table[
{x -> xmin+ix*dx, y -> ymin+iy*dy},
{ix, 0, nx}, {iy, 0, ny}
];
grid = Map[({f, g} /. #)&, grid, {2}];
Show[
Graphics[Table[
{
RGBColor[Random[], Random[], Random[]],
Polygon[{
grid[[ix, iy]],
grid[[ix+1, iy]],
grid[[ix+1, iy+1]],
grid[[ix, iy+1]]
}]
},
{ix, nx}, {iy, ny}
]],
Frame -> True
]
]
QuiltPlot[{x, y}, {x, -10, 10, 8}, {y, 5, 10, 8}]
QuiltPlot[{x^2-y^2, 2*x*y}, {x, -10, 10, 8}, {y, 5, 10, 8}]
See also 06-240/Linear Algebra - Why We Care.
Class Notes
Differentiability
Let [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ W }[/math] be two normed finite dimensional vector spaces and let [math]\displaystyle{ f:V\rightarrow W }[/math] be a function defined on a neighborhood of the point [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]
Definition:
We say that [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] is differentiable (diffable) if there is a linear map [math]\displaystyle{ L }[/math] so that
[math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{h\rightarrow0}\frac{|f(x+h)-f(x)-L(h)|}{|h|}. }[/math]
In this case we will say that [math]\displaystyle{ L }[/math] is a differential of [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] and will denote it by [math]\displaystyle{ df_{x} }[/math].
Theorem
If [math]\displaystyle{ f:V\rightarrow W }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ g:U\rightarrow V }[/math] are diffable maps then the following asertions holds:
- [math]\displaystyle{ df_{x} }[/math] is unique.
- [math]\displaystyle{ d(f+g)_{x}=df_{x}+dg_{x} }[/math]
- If [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] is linear then [math]\displaystyle{ df_{x}=f }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ d(f\circ g)_{x}=df_{g(x)}\circ dg_{x} }[/math]
- For every scalar number [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] it holds [math]\displaystyle{ d(\alpha f)_{x}=\alpha df_{x} }[/math]
Implicit Function Theorem
Example Although [math]\displaystyle{ x^2+y^2=1 }[/math] does not defines [math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math] as a function of [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math], in a neighborhood of [math]\displaystyle{ (0;-1) }[/math] we can define [math]\displaystyle{ g(x)=-\sqrt{1-x^2} }[/math] so that [math]\displaystyle{ x^2+g(x)^2=1 }[/math]. Furthermore, [math]\displaystyle{ g }[/math] is differentiable with differential [math]\displaystyle{ dg_{x}=\frac{x}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} }[/math]. This is a motivation for the following theorem.
Notation
If f:X\times Y\rightarrow Z then given x\in X we will define f_{[x]}:Y\rightarrow Z by f_{[x]}(y)=f(x;y)
Definition
[math]\displaystyle{ C^{p}(V) }[/math] will be the class of all functions defined on [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] with continuous partial derivatives up to order [math]\displaystyle{ p. }[/math]
Theorem(Implicit function theorem)
Let [math]\displaystyle{ f:\mathbb{R}^n \times \mathbb{R}^m\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^m }[/math] be a [math]\displaystyle{ C^{1}(\mathbb{R}^n \times \mathbb{R}^m) }[/math] function defined on a neighborhood [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] of the point [math]\displaystyle{ (x_0;y_0) }[/math] and such that [math]\displaystyle{ f(x_0;y_0)=0 }[/math] and suppose that [math]\displaystyle{ d(f_{[x]})_{y} }[/math] is non-singular then, the following results holds:
There is an open neighborhood of [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ V\subset U }[/math], and a [math]\displaystyle{ diffable }[/math] function [math]\displaystyle{ g:V\rightarrow\mathbb{R}^m }[/math] such that for every [math]\displaystyle{ x\in V }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ f(x;g(x))=0. }[/math].
