06-1350/Syzygies in Asymptote in Brief: Difference between revisions
From Drorbn
Jump to navigationJump to search
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===Braids=== |
===Braids=== |
||
{|align=center |
{|align=center |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|<pre> |
|<pre> |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
b.draw(); // Draw the resulting braid. |
b.draw(); // Draw the resulting braid. |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
|width="40pt"| |
|||
|[[Image:06-1350-mybraid.png]] |
|[[Image:06-1350-mybraid.png]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
===Relations=== |
===Relations=== |
||
{|align=center |
{|align=center |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|<pre> |
|<pre> |
||
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
r3.draw(); |
r3.draw(); |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
|width="40pt"| |
|||
|[[Image:06-1350-R3-asy.png]] |
|[[Image:06-1350-R3-asy.png]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 67: | Line 69: | ||
===Syzygies=== |
===Syzygies=== |
||
{|align=center |
{|align=center |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|<pre> |
|<pre> |
||
| Line 98: | Line 100: | ||
pb.draw(); |
pb.draw(); |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
|width="60pt"| |
|||
|[[Image:06-1350-bpsmall.png]] |
|[[Image:06-1350-bpsmall.png]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Latest revision as of 20:54, 4 December 2006
Installation
See 06-1350/Syzygies in Asymptote for more detailed information.
First install Asymptote. Once installed, download syzygy.asy.
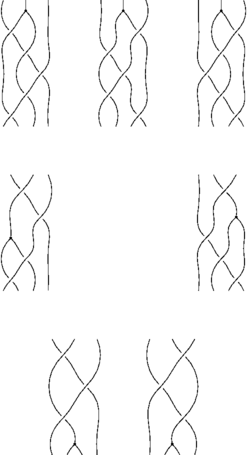
Braids
Relations
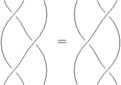
r3.toFormula() produces the formula:
r3.toLinear() produces the formula in linear form:
| [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_3(x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4) = }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ b^+(x_1,x_2,x_3) + b^+(x_1+x_3,x_2,x_4) + b^+(x_1,x_3,x_4) }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ - b^+(x_1+x_2,x_3,x_4) - b^+(x_1,x_2,x_4) - b^+(x_1+x_4,x_2,x_3) }[/math] |
and r3.toCode() produces a version usable in Mathematica:
rho3[x1_, x2_, x3_, x4_] :> bp[x1, x2, x3] + bp[x1 + x3, x2, x4] + bp[x1, x3, x4]
- bp[x1 + x2, x3, x4] - bp[x1, x2, x4] - bp[x1 + x4, x2, x3]
Syzygies
Again, like relations, we can use pb.toLinear()
| [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi B(x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4,x_5) = }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_3(x_1,x_2,x_3,x_5) + \rho_{4a}(x_1+x_5,x_2,x_3,x_4) + \rho_{4b}(x_1+x_2,x_3,x_4,x_5) }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ - \rho_3(x_1,x_2,x_3+x_4,x_5) - \rho_{4a}(x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4) }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ - \rho_{4b}(x_1,x_3,x_4,x_5) + \rho_3(x_1+x_3,x_2,x_4,x_5). }[/math] |
and pb.toCode()
PhiAroundB[x1_, x2_, x3_, x4_, x5_] :> rho3[x1, x2, x3, x5] + rho4a[x1 + x5, x2, x3, x4] + rho4b[x1 + x2, x3, x4, x5] - rho3[x1, x2, x3 + x4, x5] - rho4a[x1, x2, x3, x4] - rho4b[x1, x3, x4, x5] + rho3[x1 + x3, x2, x4, x5]
to produce formulas.