Associators with Frozen Feet
|
The Goal
The purpose of the paperlet is to find an explicit formula for an associator with frozen feet. As I'm starting to write, I don't know such a formula. My hope is that as I type up all the relevant equations, a solution will emerge. I'll be just as happy if it emerges in somebody else's mind, provided (s)he shares her/his thoughts.
|

|
| The Pentagon and the Hexagons for Parenthesized Braids | |
A horizontal associator is a solution of the pentagon equation and the hexagon equations ([Drinfeld_90], [Drinfeld_91], [Bar-Natan_97]):
| [Pentagon] |
| [Hexagons] |
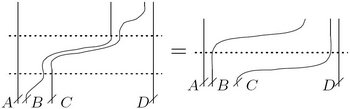
Here is the algebra of horizontal chord diagrams on vertical strands; i.e., , with , , and all different integers between and . Also, here will be (slightly different than the normal convention of , just to save some denominators).
The frozen feet quotient of any associative algebra is the quotient . (In a vertical presentation of chord diagrams we may think of the first letter of a word as its foot. The frozen feet relation makes all letters of a word commute, except perhaps the first one. "Molten bodies" is perhaps more accurate, but it is definitely less catchy).
What we are looking for is an associator with frozen feet, a solution of exactly the same equations, except regarded with the frozen feet quotients of .
Why Bother?
This isn't the place to explain the need for an explicit associator. The need is there even if it is a bit under-appreciated. Why frozen feet? Because finding an honest explicit horizontal associator seems too hard, and as a warm up and perhaps a step, it seems worthwhile to look for associators in some quotient spaces. The frozen feet quotient is the simplest quotient I'm aware off for which the answer is unknown.
Why might it be doable?
Because frozen feet are really molten bodies. It is known that there exists and associator of the form , where is some non-commutative power series with no constant term. Once the body melts (but keeping the feet frozen), this becomes
where and are commutative power series (i.e., "functions"). So finding an associator with frozen feet reduces to finding two, just two, functions of two, just two, variables, satisfying some algebraic equations. How hard can that be?
Well, it's actually even easier. Taking to be the projection from to of a group like horizontal associator we find (by means to be documented later) that me may actually take it to be of the form
| [Phi] |
where is a single unknown function of two commuting variables.
So is it doable?
Me? Why are you asking me? My forte is in daydreaming; not in solving math problems. Anyway, let's try. The hexagon equations are easier (they are written in and not the "bigger" ) and in some sense more important (they force to be non-trivial; solves the pentagon but not the hexagons), so we will start with the hexagons. First we simply the hexagon in , factor by factor:
| Factor | Written in | Comments |
| We use to write exponentials with their frozen parts made explicit | ||
References
[Bar-Natan_97] ^ D. Bar-Natan, Non-associative tangles, in Geometric topology (proceedings of the Georgia international topology conference), (W. H. Kazez, ed.), 139-183, Amer. Math. Soc. and International Press, Providence, 1997.
[Drinfeld_90] ^ V. G. Drinfel'd, Quasi-Hopf algebras, Leningrad Math. J. 1 (1990) 1419-1457.
[Drinfeld_91] ^ V. G. Drinfel'd, On quasitriangular Quasi-Hopf algebras and a group closely connected with , Leningrad Math. J. 2 (1991) 829-860.







![{\displaystyle A_{n}=\left.\left\langle t^{ij}=t^{ji}\right\rangle \right/[t^{ij},t^{kl}]=[t^{ij},t^{ik}+t^{jk}]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/79a556295f96b94ac348c88adcdd6b2222de2c9b)






























